Explore Observation Studio
Observation Studio allows users to observe their environment in a variety of ways.Dashboard shared outside of studio with commands: This dashboard is displaying data from one sensor that only records amperes. All other streams on this graph are derived by the GroveStreams derivation framework in combination with our time series rollup technique.
This dashboard can be seen live by clicking here. The update button has been disabled.
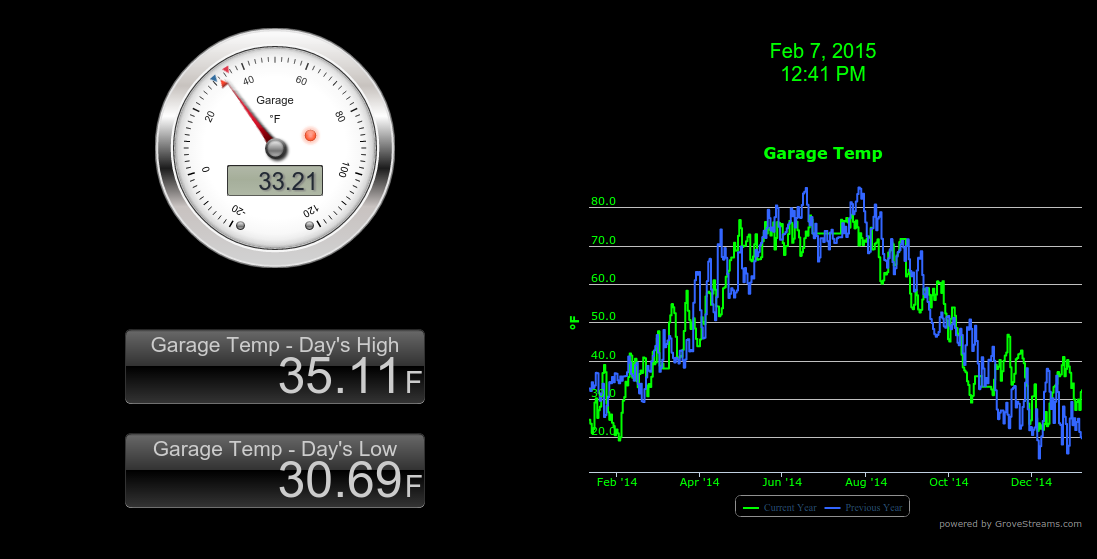
Customized Dashboard shared outside of studio: Compares last year's temperature to this year's temperature.
Styled Dashboard:
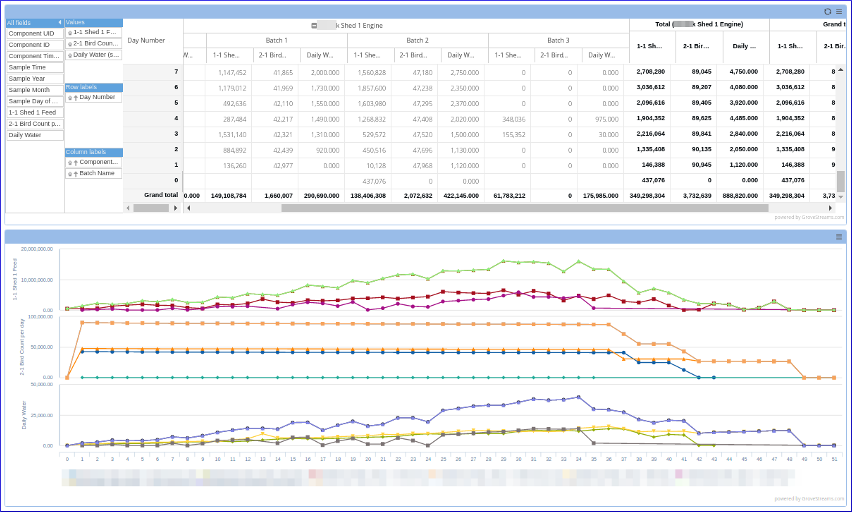
Dashboard with a Pivot Table: Dashboard pivot tables are a great way to allow users to see different views of stream data. Pivot tables allow data to be displayed as groups or in hierarchies while aggregating and displaying group sub-totals and grand-totals.
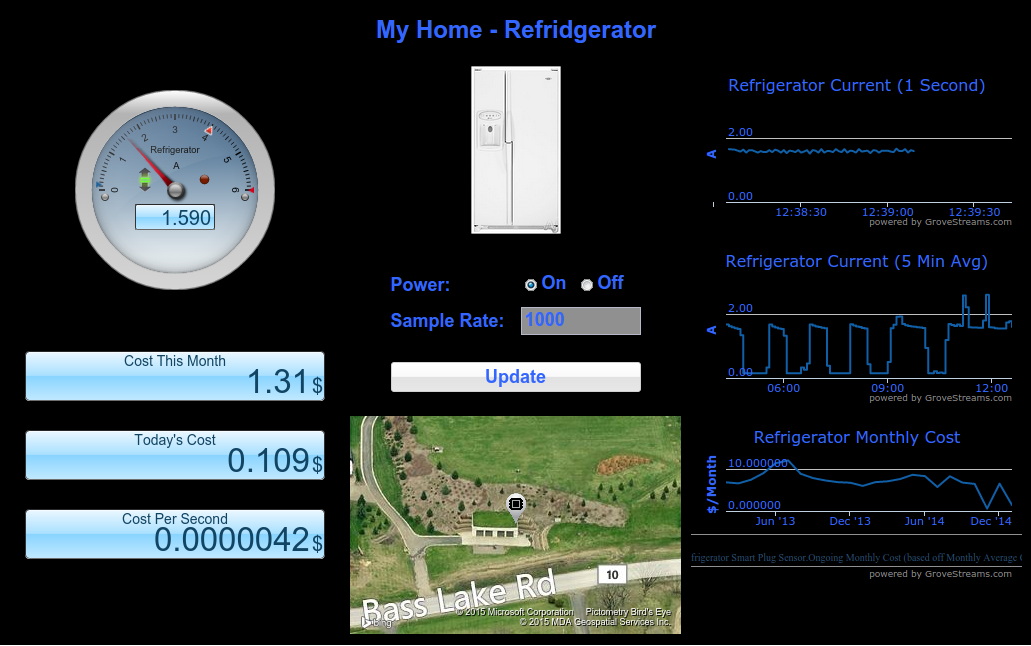
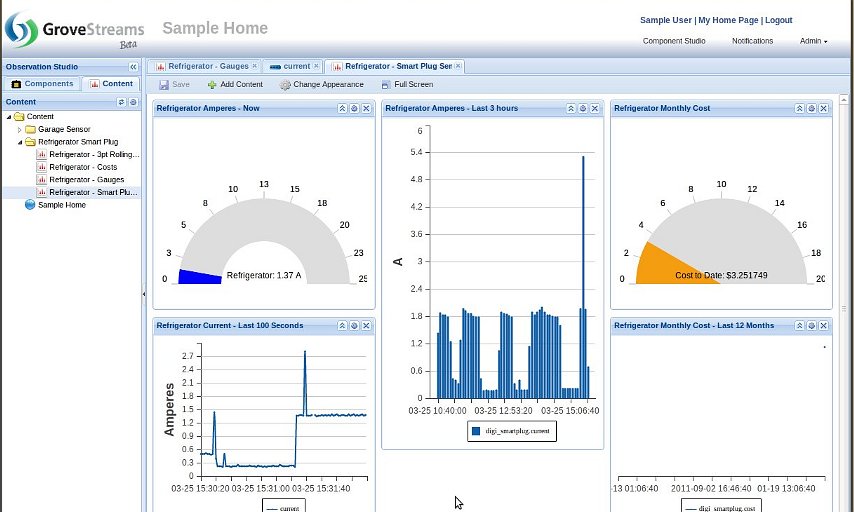
Dashboard Displaying Many Different widgets: The Refrigerator Monthly cost is slowly accruing, second by second, as one second ampere data is being uploaded into GroveStreams. Cost is a stream that is derived from the amperes stream which is converted to kWh and multiplied by a cost per kWh stream.
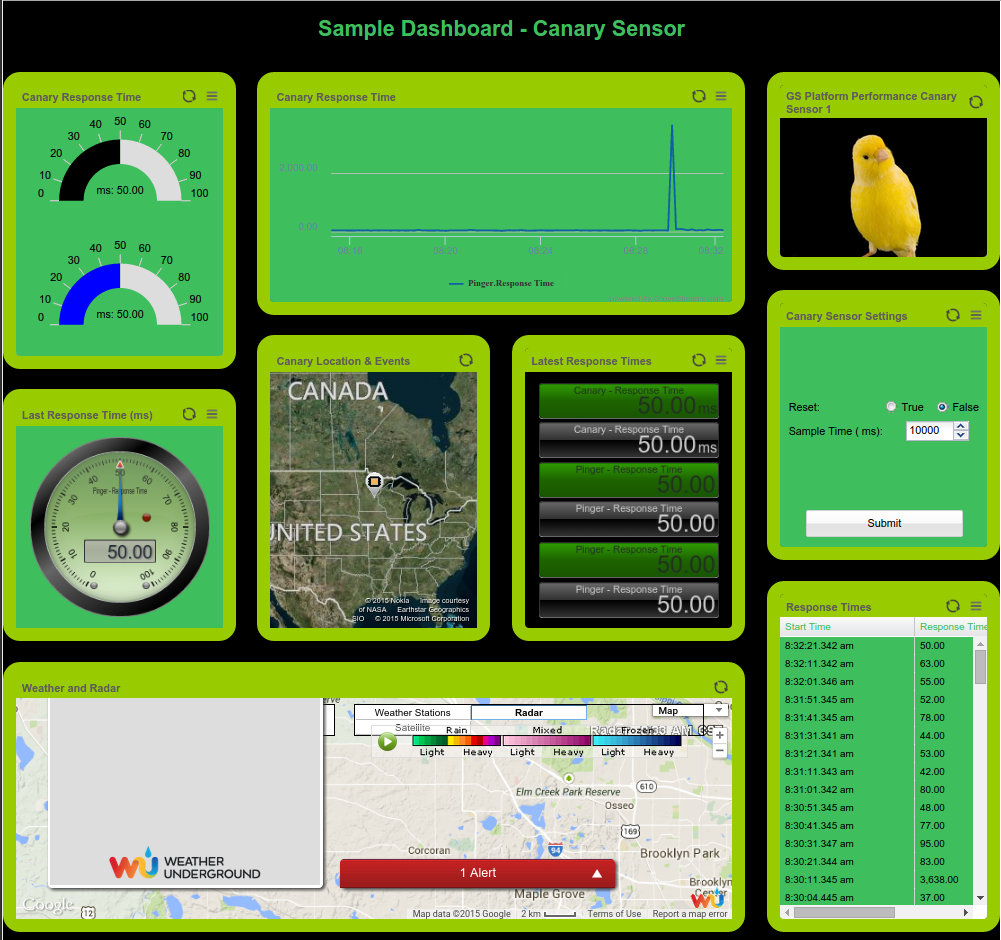
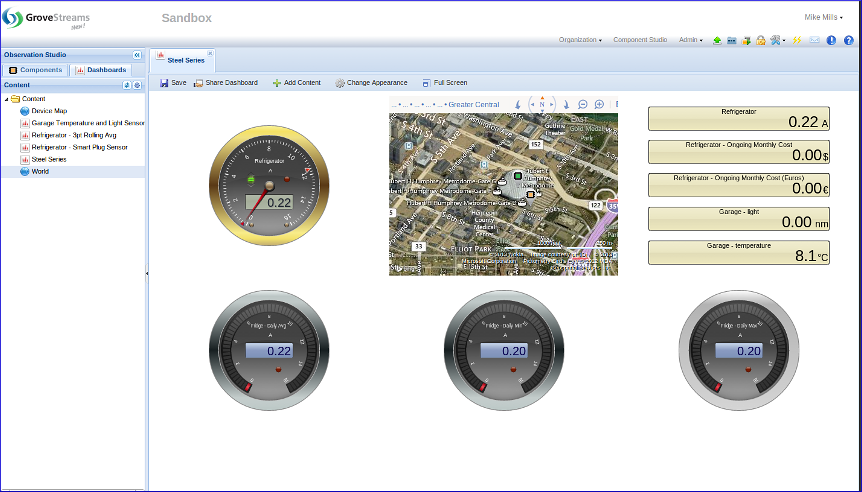
Dashboard Demonstrating some of our Steel Series widgets with a location map:
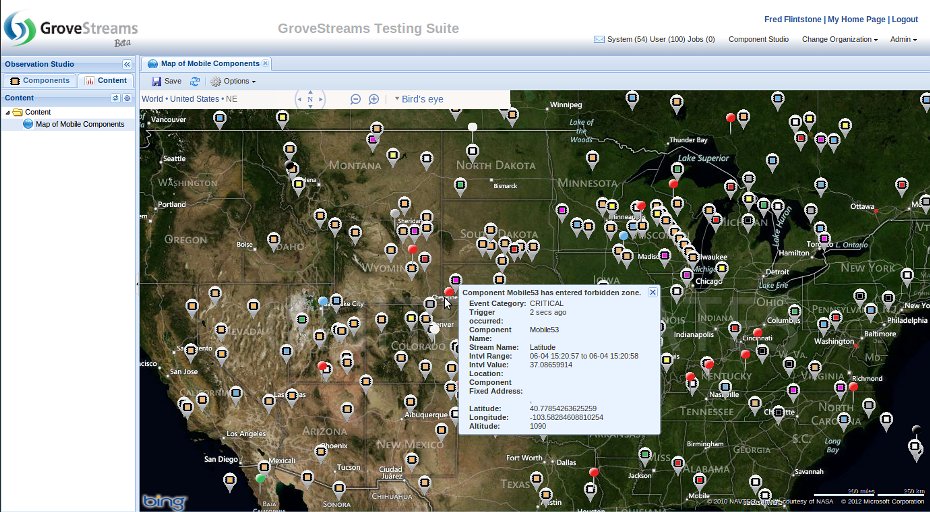
Observation Studio Maps: View a component's fixed or mobile location as data is uploaded in near real-time. Event markers will indicate where an active event started. Simply hover over one of the map's markers to get a brief description or click on the marker to get more details. Different maps can be defined and saved so that you don't have to navigate into a specific area each time you want to view a component or event's current location.
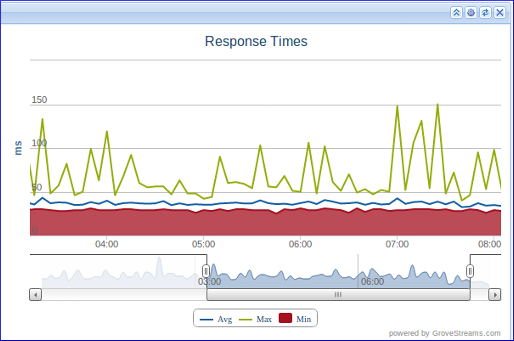
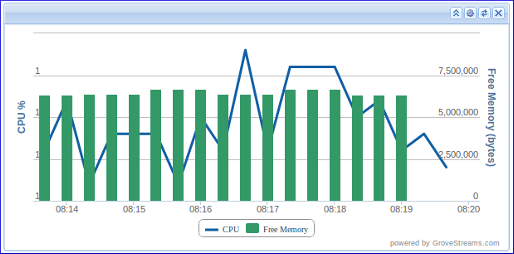
Graph Features: Multiple axes, mixed series, navigating and scrolling, zooming, and more.
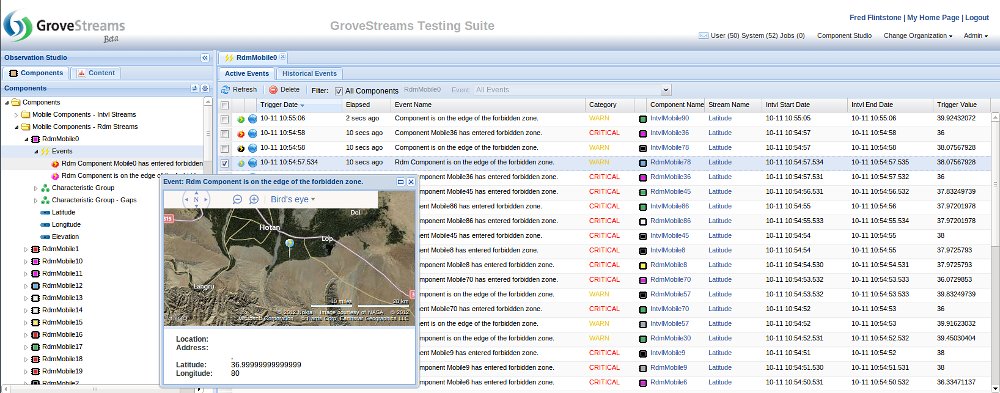
Observation Studio Events: View ongoing events and details about each event such as when and where they are occurring.
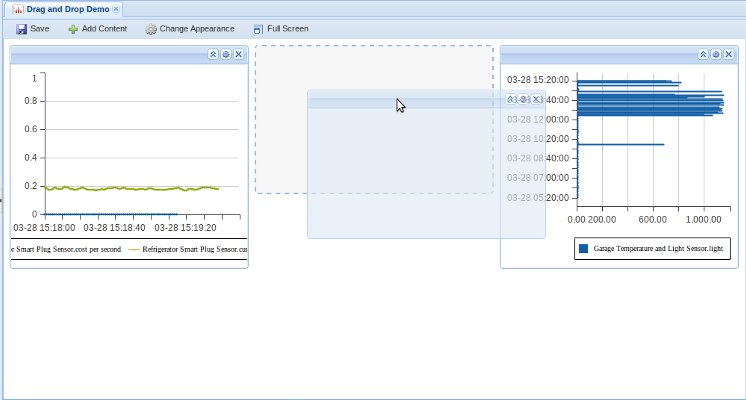
Dashboard: Users, with the appropriate rights, can create dynamic dashboards from many different widgets. Drag and drop widgets to the desired location and drag and drop one or more streams onto each widget.
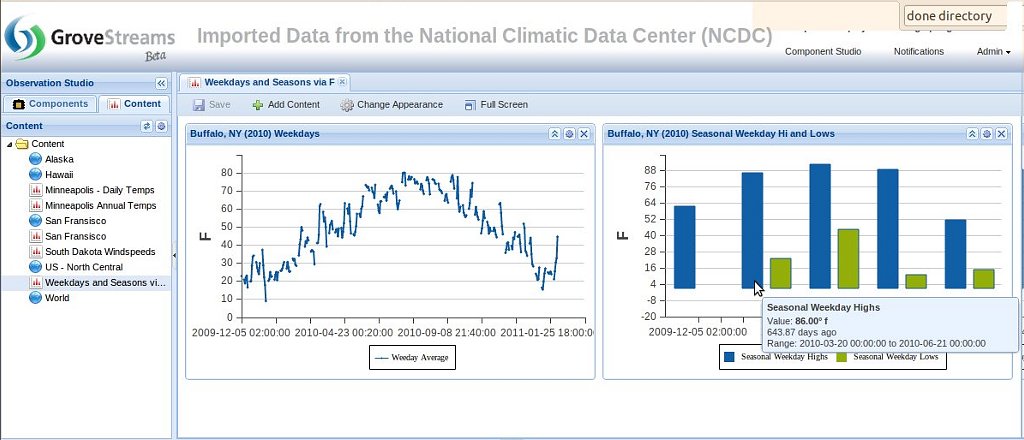
An example of a dashboard displaying a one minute base cycle weather stream that has a Time Filter constraint: Note that filtered out interval data display as gaps in the line graph.
The bar graph on the right displays a rollup of the time filter results - Seasonal Weekday Highs and Lows, which were derived from one minute weather data. These widgets have been setup as fixed time range widgets so that they can display historical results instead of 'heartbeat' reporting.
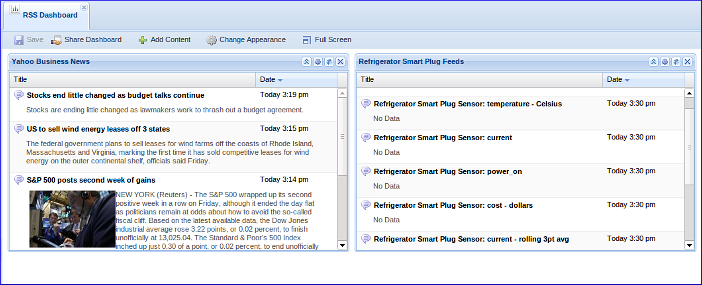
An example of dashboard RSS widgets. Display external aggregated RSS feeds or internal component or stream RSS feeds.
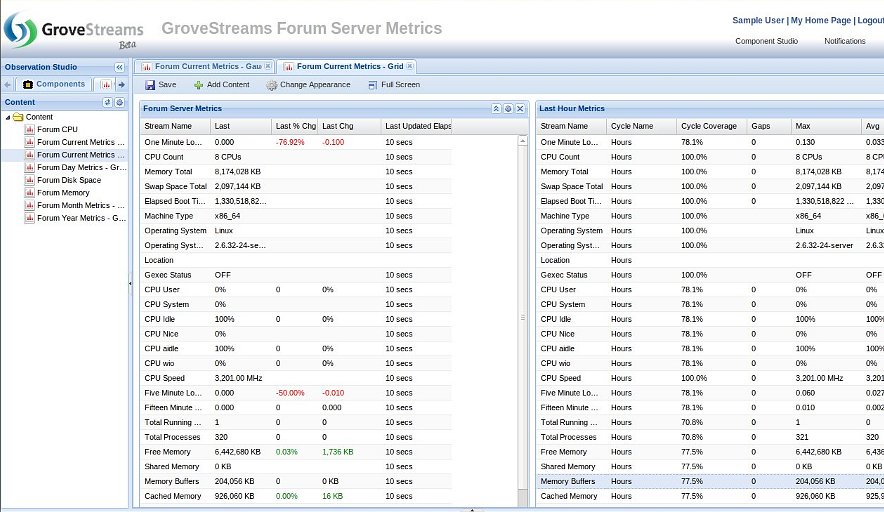
An example of dashboard grid widgets. Choose from over 50 columns of data to display within a grid widget.
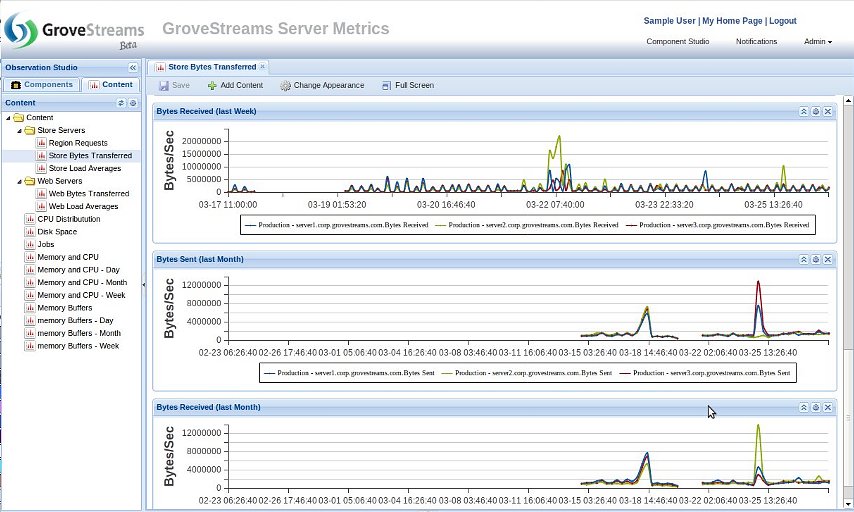
Rollup Monitoring Within a Dashboard: The below dashboard shows the power of rollups in an active widget. Each widget is displaying different rolled up time interval data which is available as data is uploaded.
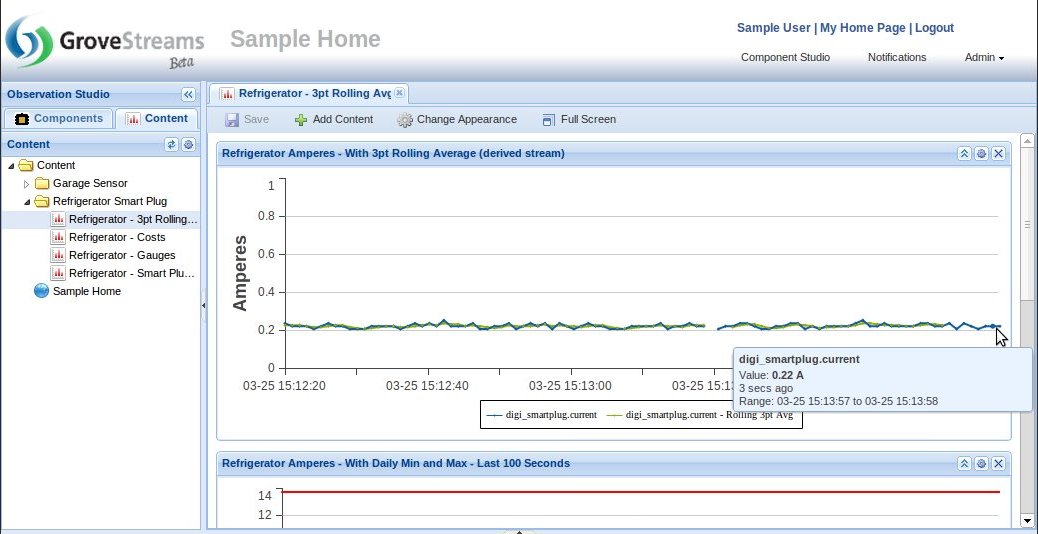
Derived Stream Monitoring within a Dashboard: This active widget is displaying base cycle stream data as it is being uploaded and it is also displaying, in the same widget, a stream derived from the base cycle stream data (3 pt rolling average). The GroveStreams derivation engine runs in parallel across all store servers every few seconds allowing derivation to occur shortly after base cycle stream data is uploaded.
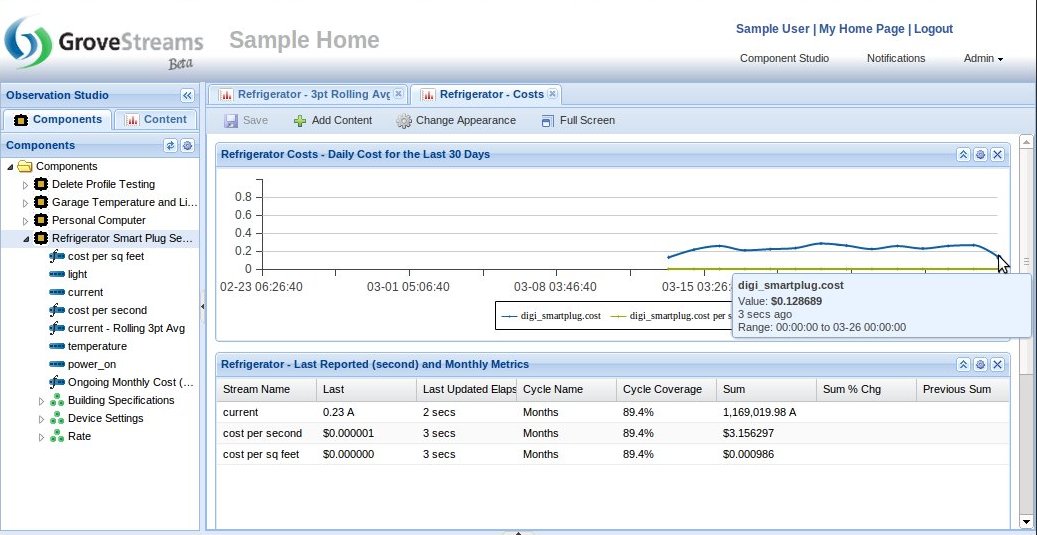
Derived Streams Monitoring Within a Dashboard: An example of an active widget displaying a derived stream, cost per sq ft, being derived from another derived stream, cost. Stream derivation only occurs when all dependent stream interval data exists for the interval being calculated. Thus a stream derived from another derived stream will be calculated shortly after its dependent derived stream is derived.
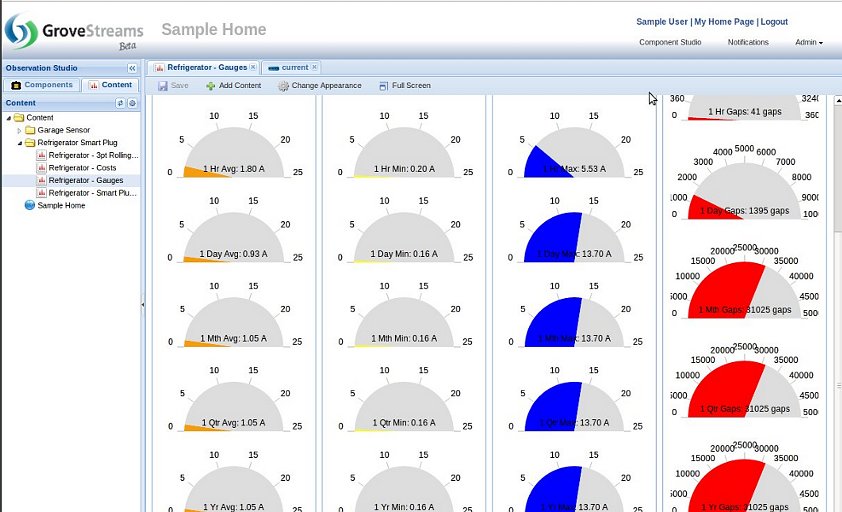
Dashboard Displaying Many Rollups from One Base Cycle Stream: The below dashboard is an example of the fraction of the amount information available for one stream associated with a rollup calendar. All of the information below is available immediately as the base cycle stream's intervals are uploaded or derived.
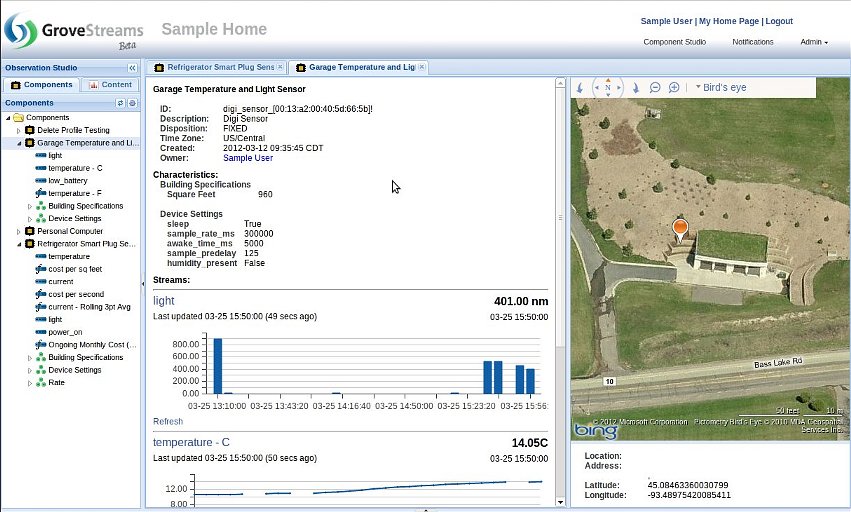
Component View: View all of a component's latest information including streams in one view. You can then click on a stream to bring up the stream view.
Stream View: Stream views allow actual data to be viewed or edited. You can also compare several streams and view rollup statistical information (minimums, maximums, min/max datetimes, gap counts, etc.).
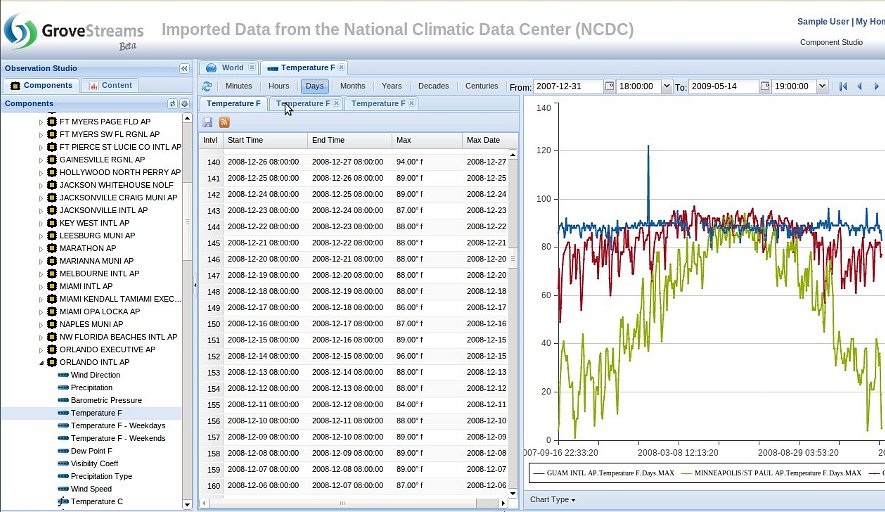
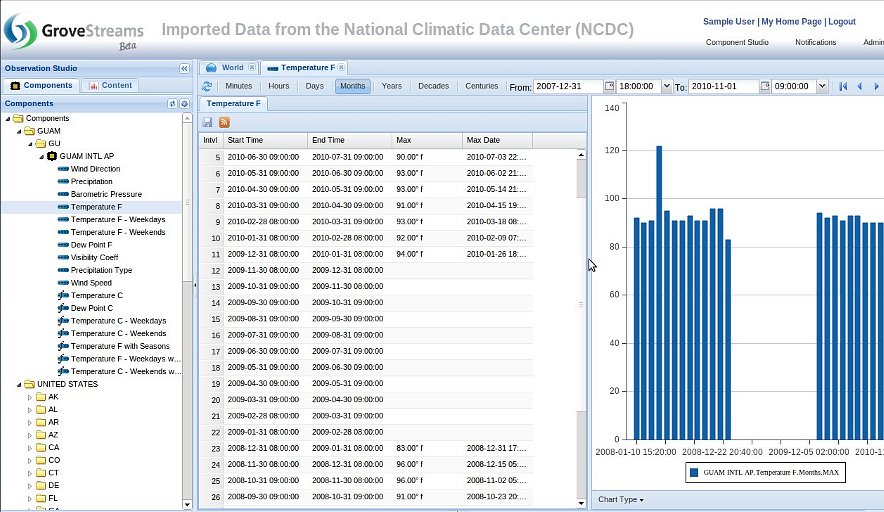
Stream View, Gaps: GroveStreams recognizes gaps in data. Below is an example of Gaps in a weather data stream. Gaps are ignored for rollup and derivation calculations. Gap count statistics are available for every rollup cycle range and can be viewed and graphed just like any other rollup statistic.
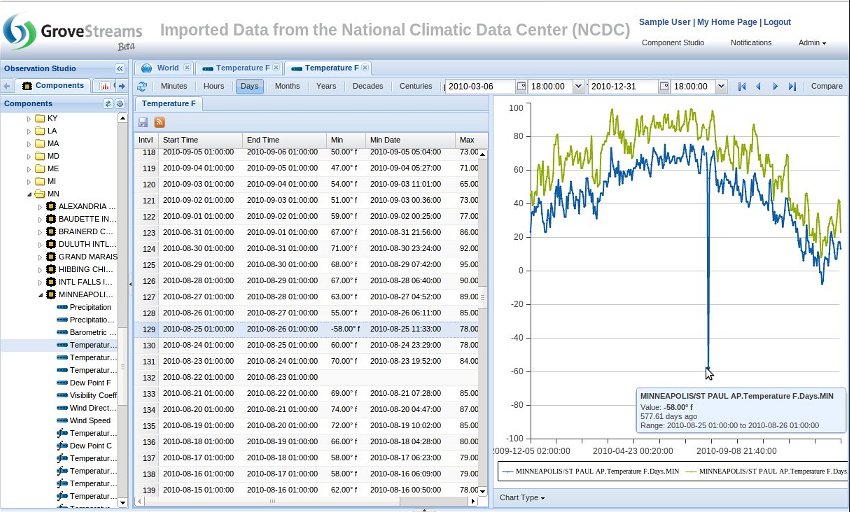
Stream View, Drill-through: An example of quickly identifying bogus data from within a graph. Hover over the suspect point and the value for that point will scroll into view and be selected on the left. Stream views support the concept of drill through. Simply click on the bogus data point within the graph and you will drill down a cycle and view the intervals that were used to calculate the rollup. Keep drilling down until you are viewing the actual uploaded value(s). GroveStreams allows you to edit any base cycle stream values and save them either within the Stream View or via our API.
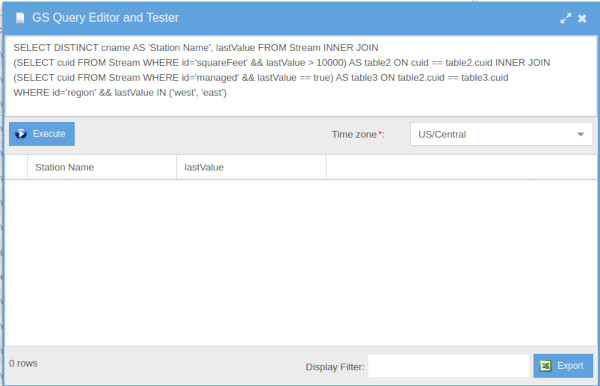
GS SQL Tester: GS SQL can be used within dashboard widgets. GS SQL can be scheduled, and the scheduled results can be included in dashboards or sent as an email.